SOLAS: Historic previous & Significance
The Worldwide Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) outlines the minimal safety necessities to be adhered to whereas establishing and dealing service supplier ships. Per the IMO Convention, signatory nations ought to ensure that their ships regulate to those necessities.
The SOLAS Convention is often thought-about a really highly effective worldwide treaty referring to the safety of service supplier vessels and seafarers.
After the massive lack of life inside the Titanic Disaster, the worldwide group wanted to establish tips and legal guidelines to cease comparable maritime accidents from occurring as soon as extra. Due to this fact, the first conference on the Safety of Life at Sea occurred in London in January 1914.
The primary SOLAS Convention was adopted on January 20, 1914, and was to enter drive in July 1915, nonetheless it was delayed on account of battle in Europe. The 2nd SOLAS Convention was adopted in 1929, coming into into drive in 1933; the third in 1948, coming into into drive in 1965; and the present mannequin was adopted in 1974, coming into into drive in 1980.
The 1960 mannequin was the first essential exercise for IMO since its establishment, as a result of it was a critical step in modernising or upgrading legal guidelines for monitoring technical developments inside the maritime enterprise.
Quite a lot of challenges wanted to be overcome, akin to conserving the convention updated by means of widespread amendments; nonetheless, their implementation took pretty a while. Due to this fact, a model new convention was adopted in 1974, which included all amendments agreed to that date along with a model new modification course of to ensure that changes have been carried out or entered into drive shortly.
The present mannequin is the 1974 one, often known as SOLAS 1974, which received right here into drive on May 25, 1980. It has been amended many cases and as of April 2022, it had 167 contracting states.
SOLAS is among the many many three most important worldwide units regulating maritime safety and marine air air pollution prevention. The alternative two are MARPOL and the STCW (Worldwide Convention on Necessities of Teaching, Certification and Watchkeeping) Convention.
Be taught: MARPOL – The Remaining Info
What is the SOLAS Convention?
SOLAS is an abbreviation for “Safety Of Life At Sea.” It is a international maritime treaty, typically often known as the SOLAS Convention or Worldwide Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), that establishes the least safety measures inside the constructing, gear, and operation of service supplier ships.
IMO SOLAS 74, the ultimate revised convention adopted in 1974, consists of quite a lot of legal guidelines beneath completely completely different SOLAS chapters, which care for safety precautions and procedures starting from the ship’s constructing to emergencies like “Abandon Ship.” The convention is updated periodically to fulfill the safety norms inside the modern supply enterprise.
This textual content explains the SOLAS chapters with a brief summary of each and likewise mentions the ideas they comprise.
Marine Notion has supplied hyperlinks to different articles which might help the readers understand how the regulation of the SOLAS Annexes is carried out on a seagoing vessel and the importance of SOLAS.
Software program of SOLAS
It applies to cargo vessels of 500 gross tonnage or further and passenger ships on worldwide journeys. Chapter 4 of the SOLAS Convention extends its scope to cargo ships with 300 gross tonnage or further. Chapter 5 applies to all vessels moreover warships, naval auxiliaries, and completely different ships owned and operated by a contracting authorities and plying on authorities, non-commercial corporations.
Compulsory Codes beneath SOLAS
- Worldwide Code for Fireplace Safety Applications (FSS Code)
- Worldwide Code for Software program of Fireplace Check out Procedures (FTP Code)
- Worldwide Maritime Code for Dry Bulk Cargoes (IMSBC Code)
- Worldwide Code Life-saving Tools Code (LSA Code)
- Worldwide Intact Stability Code (IS Code 2008)
- Worldwide Code for the Security of Ships and Port Companies (ISPS Code).
- Worldwide Code for the Growth and Gear of Ships Carrying Dangerous Chemical compounds in Bulk (IBC Code)
- Code for the Protected Carriage of Irradiated Nuclear Fuel, Plutonium and Extreme-Stage Radioactive
- Worldwide Code for the Growth and Gear of Ships Carrying Liquefied Gases Bulk (IGC Code)
- Worldwide Maritime Code for Carriage of Dangerous Objects (IMDG Code)
- Worldwide Code for the Safety of Extreme-Tempo Craft (HSC Code 1994)
- Worldwide Code for the Safety of Extreme-Tempo Craft (HSC Code 2000)
- Code for the Investigation of Marine Causalities
- Wastes in Flasks on board Ships (INF Code)
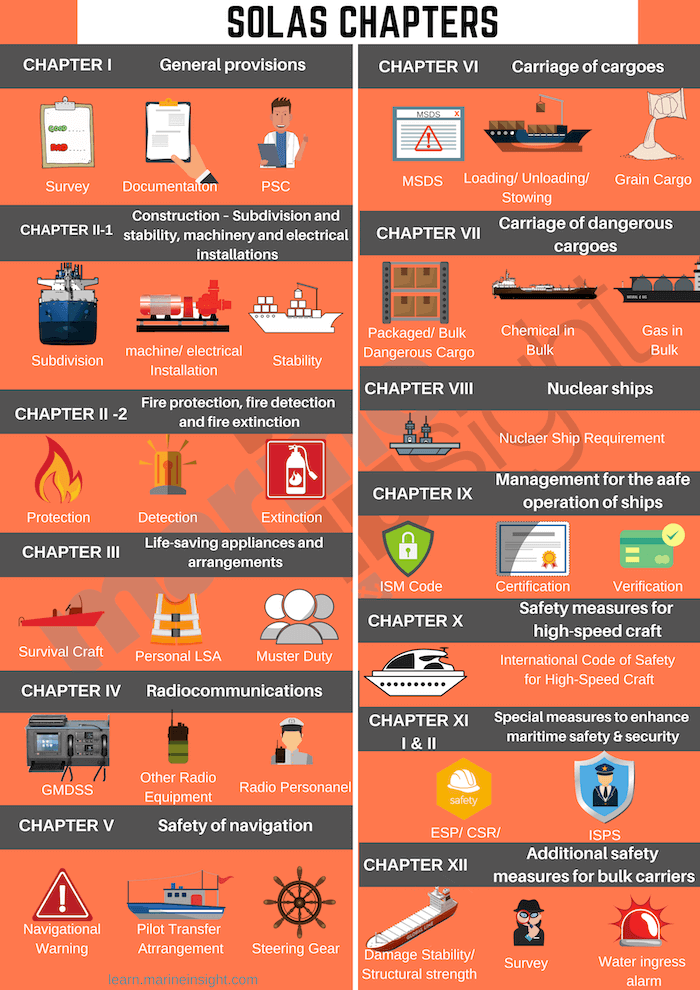
SOLAS Chapters
The SOLAS 1974 worldwide maritime treaty incorporates 13 chapters, and each chapter has its private set of legal guidelines. The subsequent is the guidelines of its14 chapters and the legal guidelines they comprise:


The Worldwide Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), 1974, describes the requirement for all service supplier ships of any flag state to regulate to the minimal safety norms laid down inside the chapters, which are as follows:
Chapter I – Primary Provisions: Surveys and certification of all the safety devices, and lots of others., are included.
Chapter II-1 – Growth – Subdivision and stability, tools and electrical installations: Presents with watertight integrity of the ship, significantly for passenger vessels.
Chapter II-2 – Fireplace security, fireside detection and extinction: This chapter elaborates on the means and measures for fireside security in lodging, cargo areas and engine rooms for passenger, cargo and tanker ships.
Chapter III—Lifesaving dwelling tools and preparations: This chapter describes all the lifesaving dwelling tools and their use in quite a few circumstances.
Chapter IV—Radio communications: This chapter consists of the requirements of GMDSS, SART, EPIRB, and lots of others., for cargo and passenger vessels.
Chapter V—Safety of navigation: This chapter provides with seagoing vessels of all sizes, from boats to VLCCs, and consists of passage planning, navigation, distress indicators, and lots of others.
Chapter VI – Carriage of Cargoes: This chapter defines the storage and securing of assorted cargo and containers nonetheless does not embrace oil and gasoline cargo.
Chapter VII—Carriage of Dangerous Objects: This chapter defines the Worldwide Maritime Objects Code for storing and transporting hazardous gadgets.
Chapter VIII – Nuclear ships: The code of Safety for a nuclear-propelled ship is claimed on this chapter.
Chapter IX – Administration for the Protected Operation of Ships: The Worldwide Safety Administration Code for ship homeowners and operators is described clearly.
Chapter X – Safety measures for high-speed craft: The safety code for high-speed craft is outlined.
Chapter XI-1 & 2—Explicit measures to bolster maritime Safety: This chapter briefs on explicit and enhanced surveys for protected operation, completely different operational requirements, and the ISPS code.
Chapter XII—Additional safety measures for bulk carriers: This chapter consists of safety requirements for bulk carriers over 150 meters in dimension.
Chapter XIII – Verification of Compliance
Chapter XIV -Safety Measures for Ships Working in Polar Waters



Contents of Each SOLAS Chapter Outlined
SOLAS Chapter I
Primary Provisions, Surveys, and Certification of all safety devices, buildings, tools, and lots of others.
This chapter is further subdivided into three parts- Half A, Half B and Half C.
Half A includes 5 legal guidelines that specify the “Software program” of this chapter to a number of forms of ships and the “Definition” of assorted terminology used inside the chapter. The regulation may not apply to all forms of vessels; subsequently, a separate half for “Exceptions” and “Exemptions” could be supplied.
All the SOLAS chapters cowl a minimal criterion for seagoing ships, irrespective of their location and nationality. It is doable that the provides or dwelling tools obtainable in a single nation shouldn’t obtainable for the ship in a foreign country. An “Equal” Half could be supplied to care for such a state of affairs.
Half B includes important legal guidelines referring to surveys and certificates that seagoing ships should have to be compliant with SOLAS. For this, 15 legal guidelines are saved beneath Half B. Legal guidelines 6 to 11 current particulars of assorted survey requirements on completely different ships, gear, tools, and lots of others., clauses on how one can do the restore, and the way a lot surveys to bear.
Related Be taught: A Guidelines of Inspections And Surveys Deck Officers On Ships Should Be Acutely aware Of
What is the Harmonised Survey System for Ships?
Regulation 12 to Regulation 18 explains the completely completely different requirements for certification obtained post-surveys.
Related Be taught: 40 Ship Certificates and Paperwork that are Checked in a Port State Administration (PSC) Survey
Regulation 19 – Administration: This regulation explains the jurisdiction of the native authorities a abroad ship is voyaging, such as a result of the coast guard, port state, and lots of others., to look at the vessel to verify its Safety. It moreover explains the steps to be taken by the federal authorities authorities to tell the concerned (subsequent port of title, proprietor, class, and lots of others.) and the way one can prepare administration.
Related Be taught: The Remaining Info to Port State Administration (PSC) Inspection on Ships
Regulation 20—Privileges: This regulation explains whether or not or not the ship can or cannot declare any privileges counting on the certificates it holds.
Half C includes only one regulation, Regulation 21, which explains how a contracting authorities can carry out an inquiry into the ship involved in an incident and causalities and what knowledge have to be collected and handed on.
Related Be taught: 10 Needed Points To Do All through Ship Collision Accident
How P & I Golf tools Work – Course of for Accident Response
SOLAS Chapter II-1
Growth – Subdivision and stability, tools and electrical installations
This chapter of SOLAS Presents with the watertight integrity of the ship, along with the passenger’s vessel and incorporates 7 components, explaining the requirements for structural, tools, electrical, stability and completely different requirements for a protected ship.
Half A includes 3 legal guidelines that specify the “Software program” of this chapter on ships as per their keel laying. The legal guidelines make clear the “Definition” of assorted terminology used inside the chapter.
Half A-1 incorporates legal guidelines explaining the requirement for the ship’s building, along with defending coating, towing preparations, deck gear fittings, constructing and drawings, and lots of others.
It moreover consists of the regulation on providing entry to completely completely different components of oil tankers and bulk carriers and the development entry information, which includes the small print of the development, along with entry plans. The tactic to assemble a ship that complies with the legal guidelines for canopy in opposition to noise could be included.
Related Be taught: Preparations For Emergency Towing Of Ship – 10 Needed Elements
Half B of this regulation explains the stableness and watertight integrity requirement. Beneath Half B 1, the legal guidelines (Legal guidelines 5 to eight) define the obligatory conditions for sustaining the intact stability of the cargo ship and passenger ship. It moreover incorporates a requirement on the information outfitted to the grasp on the vessel’s stability, explaining how one can calculate the stableness elements in quite a few conditions.
Related Be taught: Understanding Watertight Bulkheads In Ships: Growth and SOLAS Legal guidelines
Ship Stability – What Makes a Ship Unstable?
Half B 2 incorporates 4 legal guidelines (Legal guidelines 9 to 17) that make certain the watertight integrity of ships (every passenger and cargo ships) by enlisting the constructional and testing requirements of watertight and completely different very important bulkheads and the availability of the double bottom on ships’ except for tanker ships.
Related Be taught: The way in which to Check out and Hold Cargo Hatch Cowl of a Dry Ship?
Designing A Ship’s Bottom Development – A Primary Overview
Half B 3 explains the subdivision load line venture requirement for passenger ships.
Half B 4 of this chapter incorporates seven legal guidelines ( Regulation 19 to Regulation 25) for the requirement of stability administration, explaining the inspections, preventions, hurt administration drills, and information for cargo and passenger ships.
Half C focuses on completely completely different tools installations inside the engine room, along with the requirement of emergency installations inside the passenger ships from Regulation 26 to Regulation 39.
Related Be taught: 5 Phases Of Marine Tools Arrange On Ships
Half D of this chapter (from legal guidelines 40 to 45) focuses on {{the electrical}} arrange requirement for cargo and passenger ships, along with the emergency provide and preparations, along with electrical Safety and hazards.
Related Be taught: The way in which to Arrange Digital Circuits on Ship?
How is Power Generated and Supplied on a Ship?
Half E explicitly clarifies the requirement for unattended tools space beneath legal guidelines 46 to 54.
Related Be taught: Preparation for UMS Operation On Ships
Half F of this chapter particulars the selection design and affiliation for the ship’s tools and electrical system beneath regulation 55. It moreover explains the storage and distribution requirement for the low flashpoint gasoline system.
Half G explains the equipment and requirements per legal guidelines 56 and 57 for ships using low flash degree fuels.
Related Be taught: The way in which to decide on Marine Fuel Oil and Parts Important for Fuel Oil System
SOLAS Chapter II-2
Fireplace security, detection and extinction
This chapter elaborates on the means and measures for fireside security in lodging, cargo areas, and engine rooms for passengers, cargo, and tanker ships. It is divided into seven components and explains the numerous requirements for fireside safety packages put in on a ship.
Half A includes legal guidelines 1 to 3, which make clear the “Software program” of this chapter on ships’ constructing. These legal guidelines moreover make clear the “Definition” of assorted terminologies used inside the chapter and the goal and helpful requirements of this chapter.
Half B of this chapter specifies the requirement to cease fireside and explosion on cargo ships, along with tankers. It has three legal guidelines, from Regulation 4 to Regulation 6. Regulation 4 particulars how one can forestall the ignition of a flamable provide present on boats, along with the restrictions and preparations on utilizing gasoline and lube oils used onboard and the prevention of fireplace inside the cargo areas of the tanker ship.
Regulation 5 particulars curbing the unfold of fireplace on the ship. This consists of lowering anyone side of the fireside triangle to manage each the air present, oil present, or heat provide (using security provides like insulation, linings, and lots of others.) inside the doubtlessly hazardous space.
Related Be taught: 16 Fireplace Stopping Residence tools and Preventive Measures Onboard Ships
Regulation 6 of this half focuses on decreasing hazards to human life from merchandise that launch smoke and toxic gases (comparable to color, varnish, and lots of others.).
Related Be taught: 20 Hazards On Oil Tanker Ship Every Seafarer Ought to Know
Half C of this chapter incorporates 5 legal guidelines (Regulation 7 to Regulation 11) and focuses on the requirement to suppress the fireside on the earliest, along with detection and administration of smoke and flames, containment requirements, and the structural integrity of the world to cease spreading of fireplace and firefighting packages and equipment to be used on ships tools, lodging and cargo areas.
Related Be taught: Fundamentals of Fireplace Prevention Onboard Ships
Half D focuses on the escape of seafarers or passengers in case of fireplace or each different emergency. Regulation 13 explains the numerous requirements for strategy of escape for a number of forms of ships (cargo ship, passenger ship, RoRo ship, and lots of others.), gear, and packages that help in escaping from dangerous places, and lots of others.
Half E of Chapter II-2 consists of Legal guidelines 14 to 16, which give knowledge on the maintenance of the fireside detection, combating, and administration gear on cargo ships, along with tankers and passenger ships. It moreover explains the requirement for fireside safety teaching and drills on board ships. Regulation 16 focuses on the fireside safety booklet, which have to be saved on board all vessels.
Related Be taught: The importance of fireplace drills on ships
Half F of this chapter particulars the selection design and affiliation for the ship’s fireside safety beneath regulation 17.
Related Be taught: A Momentary Overview of Fireplace Administration Plan on Ship
Half G includes a specific requirement for the operations carried out on tanker and bulk service ships, akin to helicopter operations (Regulation 18), giving particulars of assorted constructing, Safety and firefighting preparations. Regulation 19 provides safety measures for carrying dangerous gadgets in containers, bulk, tanker or Roro ships.
Related Be taught: 16 Fireplace Stopping Residence tools and Preventive Measures Onboard Ships
Regulation 20 focuses on ships carrying autos and passengers, explaining the prevention, detection, and containment of fireplace on such ships. Legal guidelines 21, 22, and 23 are passenger-centric, describing the requirements a passenger ship must adjust to in case of a fireplace incident onboard ship to keep away from losing passengers and the ship from a critical accident.
Related Be taught: DNV GL: Enhancing Fireplace Safety On Ro-Ro Decks
SOLAS Chapter III
Lifesaving dwelling tools and preparations
All lifesaving dwelling tools and their use in quite a few circumstances in accordance with the ship type are described on this chapter.
This chapter has 3 Elements.
Half A includes 5 legal guidelines that specify the “Software program” of this chapter to a number of forms of ships and the “Definition” of assorted terminology used inside the chapter. The regulation may not apply to all forms of vessels; subsequently, a separate half for “Exceptions” and “Exemptions” could be supplied. Further, onboard testing and manufacturing testing procedures are moreover outlined.
Half B has 32 legal guidelines (from Regulation No. 6 to 37) on the requirements of lifesaving dwelling tools on passenger and cargo ships. Regulation 6 describes the communication dwelling tools (Radio, Pyrotechnics, and lots of others.) used for safety and lifesaving circumstances on vessels.
Related Be taught: What Are PyroTechnics on Ship?
Historic previous of Maritime Distress Indicators
Regulation 7 lists the requirement for personal lifesaving dwelling tools akin to lifejackets, lifebuoys, immersion suits and lots of others.
Related Be taught: The whole thing You Ever Wanted to Know About Life Jackets on Ships
Legal guidelines 8 to Regulation 11 comprise instructions on muster station, survival craft operation and man, and their embarkation preparations explaining the completely completely different requirements.
Related Be taught: Liferafts on Ships: SOLAS Requirements, Safety Choices & Launching Course of
Regulation 12 explicitly addresses the location of survival craft in a cargo ship (except for freefall lifeboat).
Legal guidelines 13 to 17 aspect the stowage and compulsory preparations required for the lifeboat, liferaft, marine evacuation system, restoration boat on the ship and Man Overboard Operation.
Related Be taught: Types of Lifeboats Used On Ship
Regulation 18 lists the requirements for line-throwing dwelling tools used on the ship, and Regulation 19 provides with different teaching and drill requirements for the onboard crew.
Regulation 20 utilized to all the ships for operational readiness, repairs and survey requirement of survival crafts and completely different lifesaving dwelling tools onboard the ship.
Related Be taught: Preparation For Safety Gear Survey On Ships
Life Raft Restore Firms and Repairs Procedures: A Primary Overview
Regulation 21 to Regulation 30 inform regarding the further requirement for passenger ships about survival crafts and all lifesaving dwelling tools on the passenger ships, along with drills for passengers onboard ship and helicopter operation in a passenger ship (ro-ro passenger ships of 130m in dimension have to be provided with a helicopter landing area).
Related Be taught: Cruise Ship Passenger Drill Requirements Come Into Strain On 1 January 2015
Regulation 31 to Regulation 34 describes the additional requirement for cargo ships referring to survival crafts and all lifesaving dwelling tools on the ships.
Legal guidelines 35 to 37 comprise different instructions for onboard repairs, muster lists, and lots of others. and the supply of teaching manuals and completely different onboard teaching aids on the ship.
Related Be taught: Needed Choices of Muster Guidelines on Ship
Half C of this chapter particulars the selection design and affiliation for the ship’s lifesaving dwelling tools beneath regulation 38.
SOLAS Chapter IV
Radio communications
This chapter consists of requirements of assorted radio communication gear used on board ships, akin to GMDSS, SART, EPIRB, and lots of others., for cargo and passenger vessels.
This chapter is break up into three components: Half A, Half B and Half C.
Half A includes legal guidelines 1 to 4, which make clear the “Software program” of this chapter. The foundations moreover make clear the “Definition” of assorted terminology used inside the chapter and the goal and helpful requirements of this chapter. Further, it consists of the exemptional provision and the small print of GMDSS satellite tv for pc television for computer suppliers.
Related Be taught: SOLAS requirement for World Maritime Distress Safety System (GMDSS)
Half B consists of Regulation 5, explaining the provisions of radiocommunication corporations and the identities of GMDSS by the contracting authorities.
Related Be taught: The way in which to get a GMDSS Endorsement Certificates?
Half C insists on a ship-based requirement for radio gear and incorporates 13 legal guidelines. Regulation 6 particulars radio arrange requirements on all kinds of ships, and Regulation 7 particulars the minimal requirements for varied radio gear to be used on ships.
Related Be taught: What Marine Communication Applications Are Used inside the Maritime Enterprise?
Legal guidelines 8 to 11 aspect the radio arrange performance for preliminary ship-to-shore communications and alerts in Sea areas A1, A2, A3, and A4.
Related Be taught: Introduction to World Maritime Distress Safety System (GMDSS) – What You Ought to Know
Regulation 12 lists down the additional duties of the officer on radio communication gear all through a watch.
Related Be taught: Outdated-yet-Nicely-known Marine Jobs: Radio Officers
Regulation 13 particulars the vitality provide for all the radio communication gear, along with emergency reserve provide of vitality and battery vitality.
Related Be taught: 20 Elements To Take into consideration For Coping with and Taking Care of Batteries On Ships
Legal guidelines 14 and 15 aspect effectivity necessities and maintenance required to be carried out on radiocommunication gear.
Related Be taught: On daily basis, Month-to-month And Weekly Exams Of GMDSS Gear On Board Ships
Legal guidelines 16, 17 and 18 describe the need for radio personnel qualification and completely completely different knowledge and logs, which need to be updated inside the ship log system.
Related Be taught: Needed Elements For Logbook Conserving On Ships
SOLAS Chapter V
Safety of navigation
This chapter consists of 35 legal guidelines dealing with seagoing vessels of all sizes, from boats to VLCCs. It consists of passage planning, navigation, distress indicators, and lots of others.
Legal guidelines 1 to 3 make clear the “Software program” of this chapter on the Safety of navigation. The foundations moreover define the “Definition” of assorted terminologies used inside the chapter and the goal and helpful requirements of this chapter. Further, it consists of the exemptional provision to be granted by the administration to a complying ship.
Legal guidelines 4 and 5 guidelines completely completely different navigational and mineralogical service warnings essential for a navigating officer to arrange a protected passage plan.
Related Be taught: Needed Elements For Dealing With Navigational Warnings On Ships
Legal guidelines 6, 7, 8, and 9 take care of corporations such as a result of the ice patrol service for protected navigation inside the North Atlantic, search and rescue corporations (when receiving a distress alert from the ship), the utilization of lifesaving indicators, and hydrographic corporations (for the compilation of hydrographic information and publication) by the contracting authorities.
Related Be taught: IMO Collaborates In Worldwide Implementation Of Maritime Search And Rescue
Regulation 10 particulars the ships’ routing system requirements for protected and setting pleasant navigation.
Related Be taught: IMO Adopts Key Worldwide Routing And Security Measures For Bering Sea
Regulation 11 lists the need for a reporting system to contribute in the direction of maritime and environmental Safety, the place the seagoing ship research to the concerned authorised physique.
Regulation 12 requires the contracting authorities to undertake a Vessel Guests Service (VTS) to verify protected navigation inside the coastal area, channel, port neighborhood, and area of maritime guests.
Related Be taught: What are Vessel Guests Firms?
Regulation 13 defines the place of the contracting authorities in arranging the establishment and operation of aids to navigation.
Related Be taught: Why Digital Aids of Navigation Are Needed For Ships?
Regulation 14 lists the minimal manning requirement and crew effectivity for a seagoing ship
Regulation 15 provides particulars of bridge design and procedures along with the affiliation of navigation packages and equipment.
Related Be taught: 30 Types of Navigation Gear and Property Used Onboard Stylish Ships
Regulation 16 and Regulation 17 current the need for the maintenance of navigation gear and their electromagnetic compatibility.
Regulation 18 defines the phrases for surveys, approval requirements, and effectivity necessities for navigational gear and packages, along with VDR.
Related Be taught: What Marine Communication Applications Are Used inside the Maritime Enterprise?
Regulation 19 requires a navigational system and equipment onboard the ship as of the date of constructing and as of the vessel’s gross tonnage functionality. It moreover explains the requirement for Prolonged-Differ Identification and Monitoring of Ships.
Related Be taught: The Prolonged Differ Monitoring and Identification (LRIT) System: Monitoring and Monitoring Ships
Regulation 20 explains the requirement for Voyage Info Recorder on ships for aiding in causality investigations.
Related Be taught: Voyage Info Recorder (VDR) on a Ship Outlined
Regulation 21 provides the small print of the Worldwide Code of Indicators {{that a}} radio arrange on a ship ought to hold.
Regulation 22 talks regarding the visibility requirement from the ships’ bridge window, and Regulation 23 explains the pilot change affiliation.
Related Be taught: Needed Pilot Change Preparations And SOLAS Requirements For Ships
Regulation 24 explains utilizing a heading and observe administration system when the ship is in restricted visibility or in extreme guests.
Related Be taught: 10 Needed Elements Ship’s Officer On Watch Should Take into consideration All through Restricted Visibility
Legal guidelines 25 and 26 guidelines the regulatory requirements for {{the electrical}} vitality provide, testing, and drills for steering gear packages.
Related Be taught: Means of Testing Steering Gears on Ship
Regulation 27 discusses the nautical charts and publications obtainable onboard ships for passage and voyage.
Related Be taught: Understanding the Guidelines of Passage Planning
Regulation 28 provides the small print of knowledge to be saved for all the nautical actions by the ship’s navigation officer.
Related Be taught: Utterly completely different Entries To Be Made In Bridge Log E-book of The Ship
Regulation 29 insists on the requirement for the ship’s officer to know completely completely different lifesaving indicators utilized in distress. Regulation 30 lists the operational limitations of passenger ships referring to protected navigation.
Legal guidelines 31, 32, 33 and 34 comprise a requirement for the grasp of the ship on how one can act in a dangerous state of affairs by sending hazard message (whereas encountering any dangerous navigation state of affairs to the contracting authorities using a message or Worldwide code of Signal. It moreover consists of the sort of knowledge which have to be despatched to the authorities.
Further, the regulation moreover explains the obligations/ procedures for aiding the ship in peril and the way one can steer clear of a state of affairs which will flip right into a hazard. Regulation 35 strictly prohibits utilizing distress indicators for any goal except for these outlined inside the above legal guidelines.
Related Be taught: What is the obligation of the Grasp after Abandoning a Ship?
SOLAS Chapter VI
Carriage of Cargoes and Oil Fuel
This chapter of SOLAS defines the storage and securing of assorted cargo and containers nonetheless does not embrace oil and gasoline cargo. It is further divided into three components: Half A, Half B, and Half C.
Half A includes Regulation 1 to Regulation 5. Regulation 1 explains the “Software program” of this chapter, the “Definition” of assorted terminology used inside the chapter, and the requirements to carry steady cargo except for grain.
Regulation 2 tells regarding the knowledge alternate between the shipper and the grasp on the loaded cargo type.
Related Be taught: What’s Ship-Shore Interface Administration inside the Transport World?
Regulation 3 explains the need for an Oxygen analyser and completely different gasoline detection gear to watch these steady cargoes emitting toxic or flammable gases.
Regulation 4 describes the small print of using pesticides on ships for fumigation capabilities.
Regulation 5 provides knowledge on stowing and securing cargo. It moreover lists the MSDS requirement for oil gasoline carried on board a ship. Further, it explains the need to ban mixing bulk liquid cargo and manufacturing processes all through sea voyages.
Related Be taught: Supplies Safety Info Sheet or MSDS Used on Ships
Half B of this SOLAS chapter lists the actual provisions for carrying steady bulk cargo. It consists of Legal guidelines 6 and 7, which make clear the method for accepting a cargo and the way one can load and unload such cargo.
Related Be taught: 9 Frequent Hazards Of Bulk Cargo On Ships
Half C focuses on the requirement for the Carriage of grains beneath Legal guidelines 8 and 9, which provides the definitions of the Worldwide Grain Code and completely different essential phrases related to grains ailing with the requirements to carry grain cargoes on the ship.
Related Be taught: 23 Needed Maritime Codes Used inside the Transport Enterprise
SOLAS Chapter VII
Carriage of dangerous gadgets
Defines the Worldwide Maritime Objects Code for storing and transporting dangerous gadgets.
This chapter is further divided into 4 components: Half A, Half B, Half C and Half D.
Half A provides knowledge on the Carriage of dangerous gadgets inside the packaged sort beneath seven Legal guidelines. 1, 2 and three make clear the “Software program” of this chapter and the “Definition” of assorted terminology used inside the chapter, along with the requirements to carry dangerous gadgets inside the packaged sort.
Related Be taught: 8 Points Deck Officers Ought to Know Whereas Coping with Packaged IMDG Cargo
Regulation 7 is dedicated to the Carriage of dangerous gadgets in steady bulk sort. It defines the phrases used beneath this regulation. It further explains the documentation and stowage with segregation requirements for such cargoes. The reporting of the incident and completely different conditions related to the damaging gadgets carried in steady bulk sort could be supplied.
Related Be taught: A Info To HAZMAT Cargo Loading On Ships
Half B of this chapter explains the event and equipment for carrying dangerous liquid chemical compounds in bulk. Legal guidelines 8, 9 and 10 define the Definition” of assorted terminology used inside the chapter and the equipment of this chapter along with the requirements for chemical tankers which carry such cargoes.
Related Be taught: A Info To Plan Stowage On Chemical Tankers
Half C of this chapter explains the event and equipment for carrying liquified gasoline in bulk as cargo. Legal guidelines 11, 12, and 113 define the completely completely different terminology used inside the chapter, the “Software program” of gasoline ships, and the requirements for gasoline tankers carrying such cargoes.
SOLAS Chapter VIII
Nuclear ships
The code of Safety for the nuclear-propelled ship is claimed on this chapter.
This chapter consists of 12 legal guidelines explaining the equipment, exemptions, approvals, and requirements (for reactor installations), Safety in opposition to radiation, safety analysis, working information, surveys and certifications, Controlling authority and steps in case of any causality as a consequence of radiation, and lots of others.
Related Be taught: Understanding Nuclear Marine Propulsion
SOLAS Chapter IX
Administration for the Protected Operation of Ships
The Worldwide Safety Administration Code for ship homeowners and operators is described clearly. Legal guidelines 1 and a few of this chapter make clear the small print regarding the “Software program” of SOLAS Chapter 9 and the “Definition” of assorted terminology used inside the chapter.
Regulation 3 requires compliance with the ISM code, adopted by essential certifications in Regulation 4, which embrace DOC, SMC, and lots of others.
Related Be taught: How is ISM Code Utilized On Ships?
Legal guidelines 5 and 6 lists the maintenance of conditions and verification & administration, respectively.
Related Be taught: What Is Safety Administration System (SMS) On Ships?
SOLAS Chapter X
Safety measures for high-speed craft
This chapter is dedicated to high-speed crafts solely. It explains the safety requirements and incorporates three legal guidelines deciphering the Definitions of assorted terminology used inside the chapter and the “Software program” of high-speed craft along with the requirements for high-speed crafts.
Related Be taught: Boats with a Distinction: The Extreme-Tempo Crafts
SOLAS Chapter XI
This chapter is break up into two sections.
Half one, i.e. Chapter XI -1, provides with the Explicit measures to bolster maritime Safety, along with Explicit and Enhanced surveys for protected operation. The second a part of this SOLAS chapter, Chapter XI-2, lists the legal guidelines for explicit tips to reinforce maritime security.
Chapter XI-1 consists of seven legal guidelines. Regulation 1 provides particulars in regards to the authorisation of a recognised organisation. Regulation 2 compiles the requirements for the improved survey for bulk carriers and oil tankers and harmonises the survey durations of ships not subjected to the ESP code.
Related Be taught: What is the Enhanced Survey Programme (ESP)?
Regulation 3 provides the ship identification amount and agency cum proprietor identification amount.
Related Be taught: Computerized Identification System (AIS): Integrating and Determining Marine Communication Channels
Regulation 4 explains the place of Port state administration on operational requirements.
Regulation 5 provides with the continuous synopsis report, which is obtainable onboard as a historic overview of the ship knowledge.
Related Be taught: What’s Regular Synopsis Report (CSR) of Ships?
Regulation 6 specifies the additional requirement for investigating marine causality and incidents.
Related Be taught: A Seafarer’s Place in Gathering Proof All through Maritime Accidents
Regulation 7 describes the requirement for ambiance testing units for enclosed areas for measuring oxygen, flammable gases, H2S, Carbon monoxide, and lots of others.
Related Be taught: IMO: Enclosed Home Ship Safety Rule Enters Into Strain
Chapter XI-2 provides with maritime security measures that every one the occasions involved in a naval commerce should adjust to, i.e. ship, port, shipowner, contracting authorities and authorities. This SOLAS chapter consists of 13 legal guidelines, and Legal guidelines 1 and a few make clear the Definition” of assorted terminology used inside the chapter and the small print regarding the “Software program” of this chapter.
Regulation 3 focuses on the contracting authorities stating their obligation in path of maritime security.
Regulation 4 lists the requirements for companies and ships to regulate to the ISP’s code, adopted by Regulation 5, which provides with the companies’ explicit obligation in path of maritime security.
Related Be taught: The ISPS Code For Ships – An Necessary Quick Info
Regulation 6 specifies the essential requirement for all seagoing ships regarding the Ship Security Alert System (SSAS).
Related Be taught: What’s a Ship Security Alert System (SSAS)?
Regulation 7 provides with threats to the vessels, and the contracting governments should set a security stage for them.
Related Be taught: What Are The Security Ranges Beneath ISPS Code?
Regulation 8 lists down the discretion of the grasp for bearing in mind ship safety and security.
Regulation 9 explains the compliance and administration measures a ship must exhibit in port, and Rule 10 states the associated requirements for port facilities beneath the ISP’s code.
Related Be taught: 10 Strategies to Enhance Ship Security
Legal guidelines 11 and 12 communicate regarding the varied and equal security affiliation by the contracting authorities and administration.
Regulation 13 provides with the completely completely different knowledge that have to be communicated to the ship and ship supervisor.
Related Be taught: What’s Ship Security Analysis (SSA)?
SOLAS Chapter XII
Additional safety measures for bulk carriers
This chapter consists of 14 legal guidelines and consists of safety requirements for bulk carriers with a dimension of better than 150 m.
Legal guidelines 1,2, and three aspect the “Definition” of assorted terminology used inside the chapter and the small print regarding the “Software program” of this chapter, adopted by the implementation schedule for the survey as per the date of constructing.
Regulation 4 The hurt stability requirements for bulk carriers are outlined on this regulation.
Related Be taught: Ship Stability: Damaged Stability of Ships
Legal guidelines 5 & 6 aspect structural vitality and completely different structural requirements for bulk service ships.
Related Be taught: Understanding the Design Of Bulk Carriers
Regulation 7 provides with the surveys and maintenance requirements of the bulk carriers, adopted by Regulation 8, which explains the information on compliance for bulk carriers.
Related Be taught: 9 New Options of IACS Harmonised Frequent Structural Pointers (CSR) For Ships
Regulation 9 focuses on these bulk service ships unable to regulate to regulation 4 because of the design of cargo holds. Code 10 lists the requirement for declaring the steady bulk cargo density.
Regulation 11 particulars the loading units used for cargo loading on bulk service ships.
Related Be taught: 11 Steps to Enhance Safety of Bulk Supplier Ships
Regulation 12 lists the phrases for having a water ingress alarm in holds, ballast space and completely different dry areas in a bulk service ship.
Regulation 13 applies to all bulk carriers irrespective of their date of constructing and explains the necessity of pumping packages to empty the ballast tanks.
Related Be taught: A Info To Ballast Tanks On Ships
Regulation 14 focuses on the restrictions on bulk service ships from crusing with an empty cargo keep.
Related Be taught: 9 Frequent Hazards Of Bulk Cargo On Ships
Aside from the above SOLAS 12 Chapters, the below two are thought-about SOLAS new chapters added in latest instances.
SOLAS Chapter XIII
Verification of Compliance
This chapter was adopted on 22 May 2014. It requires all Contracting Occasions to endure periodic audits by the licensed organisation following the audit customary to substantiate compliance with and implementation of the present Convention.
This chapter consists of legal guidelines 1 to 3 explaining the “Definition” of assorted terminologies used inside the chapter and the small print regarding the “Software program” of this chapter, adopted by the verification system for contracting authorities.
Related Be taught: Compulsory Audits And Totally different Amendments Enter Into Strain On 1 January 2016
SOLAS Chapter XIV
Safety Measures for Ships Working in Polar Waters
It provides with the ships working in Arctic and Antarctic waters and the need to hold a Polar Ship Certificates.
This Code entered into drive on 1 January 2017 and outlined to shipowners and managers the steps to take to verify their ships’ compliance with the completely completely different courses. It’s no doubt one of many latest chapters launched inside SOLAS in 2017.
It incorporates 4 Legal guidelines, starting from legal guidelines 1 and a few, which aspect the definitions of the terminology used on this chapter and the equipment of this code.
Related Be taught: The IMO Polar Code In Strain, Beginning 1 January 2017: How To Comply
Regulation 3 explains the requirements for ships to which this chapter applies, adopted by regulation 4, which suggests the phrases for varied design and affiliation for vessels crusing in Arctic and Antarctic areas.
You may also want to read-


A Freshmen Info To Maritime Laws
- Maritime concepts and legal guidelines for Worldwide commerce
- Needed for supply companies, seafarers and shore workers
- Be taught Instantly
- 2 FREE Bonuses
- Assured For 30 Days
Disclaimer :
The info contained on this site is for fundamental knowledge capabilities solely. Whereas we endeavour to take care of the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any selection, particular or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the site or the information, merchandise, corporations, or related graphics contained on the net website for any goal. Any reliance you place on such knowledge is subsequently strictly at your particular person hazard.
In no event will we be answerable for any loss or hurt along with with out limitation, indirect or consequential loss or hurt, or any loss or hurt in any method arising from lack of understanding or earnings arising out of, or in reference to, utilizing this site.
Disclaimer :
The info contained on this site is for fundamental knowledge capabilities solely. Whereas we endeavour to take care of the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any selection, particular or implied, regarding the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the site or the information, merchandise, corporations, or related graphics contained on the net website for any goal. Any reliance you place on such knowledge is subsequently strictly at your particular person hazard.


About Creator
Raunek Kantharia is a marine engineer turned maritime creator and entrepreneur. After a brief stint on the ocean, he based mostly Marine Notion in 2010. Aside from managing Marine Notion, he moreover writes for lots of maritime magazines and websites.
Be taught Additional Articles By This Creator >
On daily basis Maritime Info, Straight To Your Inbox
Sign Up To Get On daily basis Newsletters
Be part of over 60k+ people who be taught our daily newsletters
By subscribing, you adjust to our Privateness Protection and can acquire occasional deal communications; you could unsubscribe anytime.